Headings
Headings
Web A11y Checklist
- Overview
- Where do I start?
- Build structure/content
- Provide alternative means of accessing information
- Use color appropriately
- Make tables/docs accessible
Headings are important, as they create a structure that allows screen readers to navigate your site. They also improve the usability of your site, making it easy for viewers to find the information they need.
Appropriate use
Code example: You should use the appropriate heading tag, as outlined below. You can style these in your .CSS file to adjust the look and feel of each heading level.
<h1> Main Topic </h1>
Appropriate nest headings: Each heading should be appropriately nested as in the example below, following a logical order.
<h1> Main Topic </h1>
<h2> Comparison </h2>
<h3> Reason 1 </h3>
<h3> Reason 2 </h3>
<h2> Contrast </h2>
Use concise language: It is important as you label your headings to use concise language. For example, instead of a section being titled “How Students can enroll in our summer camp program” you can reword this to “Enrolling in Summer Camp.”
How to test for compliance
We recommend using the Skip to Headings browser extension on Google Chrome. This will allow you to visually see the heading structure on your page.
Common mistakes
Empty headers: A common mistake occurs when a heading is deleted in a content management system, but the formatting remains. This leaves behind an empty heading, which can appear as “[Empty Text Content]” when using the Skip to Headings plugin.
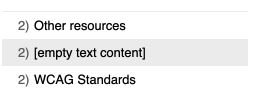
If you click on the empty link (in the Skip to Headings plugin) it will take you to that spot on the page, where you can view the code. It will likely look like the following:
<h2> </h2>
<p> Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor
incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud
exercitation ullamco laboris nisi ut aliquip ex ea commodo consequat. </p>
Improperly nested headings
Using the plugin you can also see where you may have improperly nested headings, for example going from H1 to H3.